NovaBay’s Robust Clinical Pipeline Approaches Critical Clinical Trial Results in 2013
Investment Thesis
NovaBay has just received approval in the US for its first product NeutroPhase and will be commercializing it throughout the world using regional partnerships. It has a much more important second product, NVC-422, which is being developed for three distinct disease indications: as a dermal gel for the skin disease impetigo, an eye drop for viral conjunctivitis and an instillate for treating urinary catheter encrustation and blockade or UCBE.
I believe that NovaBay (NBY) is significantly undervalued at its current market capitalization of just $37 million. In this report, I highlight its four product opportunities and estimate the value of each using a discounted cash flow analysis. Their potential value based on my analysis several times the current market capitalization.
Investors are awaiting with great interest results from a phase IIb/III impetigo trial in 2Q, 2013 and a phase IIb/III conjunctivitis trial in 3Q, 2013. Important phase II data for NVC-422 in UCBE should be reported in 1H, 2013. Clinical trial results should give investors the data needed to assess the potential for approval and commercial sales of NVC-422 in these three indications. Needless to say, 2013 is a big year for NovaBay.
The company appears to need more capital to support operations in 2013. I am expecting an equity offering of $10 million sometime later this year or in early 2013. At the current price of $1.30 and assuming 50% warrant coverage; this could increase the fully diluted share count by 11.5 million shares to 46.4 million shares. This is factored into my calculations.
This financing overhang has been and may continue to be a headwind. With its completion, the stock performance in 2013 will be determined by the phase IIb/III trial results for NVC-422 in impetigo and viral conjunctivitis. I think that it both trials are successful, the stock could trade above $5 and if both fail, it could fall to the $0.50 to $0.75 range based primarily on the potential for NeutroPhase. I think this offers a very favorable risk reward ratio.
Valuation Methodology for NovaBay
NovaBay is a complex company to understand because of the three product opportunities associated with NVC-422 and the additional opportunity of NeutroPhase; it is effectively four companies in one. Each of these has differing commercial prospects. In order to frame the potential value of each of these assets, I have started with the hypothesis that each of NVC-422 clinical trials now underway will be successful and have built a sales model for its use in impetigo, viral conjunctivitis and UCBE. I have then estimated what the resultant royalty stream or operating income stream could be over the patent life of the products. This is summarized in Table 1.
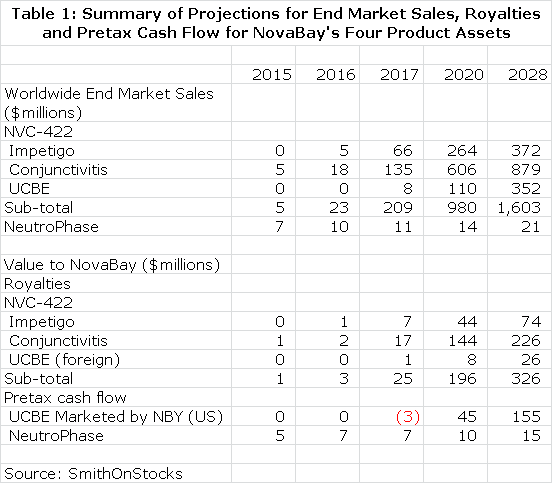
I discounted the future stream of royalties and operating cash flow to determine a net present value for each product using discount rates of 10% and 15%. This seems a reasonable range of discount rates to use as compared to current risk free bond yields of about 3%. This is shown in Table 2. Please note that all calculations of net present value are on a pretax basis.
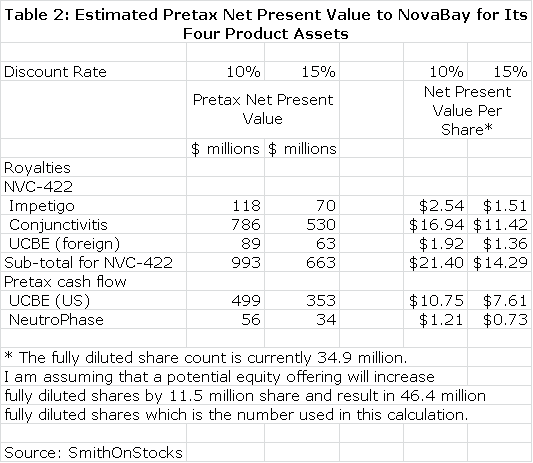
I want to re-emphasize to investors that the above tables assume success in each of the clinical trials that report topline data in 2013, but there is no guarantee that any of these trials will succeed. I believe that the impetigo trial has the highest probability for success as I explain in this report. I am more cautious on the viral conjunctivitis and urinary catheter blockage and encrustation trials. NeutroPhase is in a commercialization stage and has already begun to create revenues. The probability of its achieving my projections is good in my opinion. I would urge the reader to carefully read later sections of this report which explain in greater detail the reasoning underlying the projections in tables 1 and 2.
Table 2 gives the impression of great precision that is not really the case. The reader should also be aware that all the numbers are pretax and not adjusted for taxes. I think the importance of the table is that it gives a sense of the relative importance of the business opportunities NovaBay enjoys and certainly underlines the impressive breadth of opportunities. Some key observations from table 2 are as follows:
- The potential of NeutroPhase alone comes close to justifying the $37 million market valuation of the company.
- If the impetigo phase IIb/III trial results are positive, it should lead investors to conclude that the NVC-422 is approvable. I believe that this this along with NeutroPhase could increase the stock price to $2.00 or more.
- Success in the conjunctivitis indication for NVC-422 could have an enormous impact on the market valuation and could possibly drive the stock over $10. This is a homerun opportunity. The results of the phase IIb/III viral conjunctivitis trial should be reported by 3Q, 2013.
- NovaBay has indicated that it may build a commercial sales force to market NVC-422 for the UCBE indication in the US. This is second only to the viral conjunctivitis indication in potential as a successful commercial organization creates much more value than licensing.
- If all of these four development efforts are successful, the combined net present value on an after tax basis is over $30 per share.
Clinical Trial Timelines Provide Important 2013 Investment Determinants
Galderma is NovaBay’s partner for NVC-422 in impetigo and is funding and conducting clinical trials. It began enrolling a phase IIb/III trial in September 2012 for NVC-422 applied as a dermal gel for the treatment of impetigo. The trial could complete enrollment of 350 patients in 2Q, 2013 with topline data available in 3Q, 2013. This is a randomized, placebo controlled trial that could support registration. I expect that most regulatory agencies will require a second supporting trial, which could be started in 2H, 2013. If both trials are successful, I think US approval could come in 2016.
NovaBay started a phase IIb/III trial in May 2012 for NVC-422 to treat viral conjunctivitis. This trial will enroll 450 patients and topline data is expected in 2H, 2013. Success in this trial could lead to a partnering deal in late 2013 or early 2014. As with the development in impetigo, I think that a second supporting trial will be needed for most regulatory agencies to grant approval. This second trial could start in late 2013 or early 2014. If both trials are successful, I think US approval could come in 2016.
A phase II trial in urinary catheter encrustation and blockade has already reported encouraging data in 20 patients. Results in additional patients will be reported in 1Q, 2013. In addition to data on more patients, this part of the trial has more substantial and meaningful endpoints. It is also using a higher concentration of drug which could improve results and possibly establish that two times a week dosing is effective. Assuming success in the clinical development program, approval in the US could come in 2017. NovaBay may commercialize NVC-422 in the US on its own.
NovaBay has just received US approval for NeutroPhase for the cleansing and treatment of wounds resulting from surgery, trauma or disease. I am expecting a US partnering deal soon and introduction in the US in 1Q, 2013. It is already partnered in China and other deals are being negotiated throughout the world.
Why Hasn’t The Stock Done Better?
One would think that with NeutroPhase beginning commercialization and the late stage trials of NVC-422 in impetigo and viral conjunctivitis that NovaBay would be valued at more than its current market capitalization of $37 million.
However, the company has not yet caught the attention of Wall Street and it is followed by only one analyst. I believe that the lack of awareness is partially a function of its complexity. NovaBay is essentially four companies in one and requires a great deal of research to understand each of its components.
Biotechnology investors have learned through hard experience that small companies sometimes exaggerate the depth and maturity of their pipelines. This innate skepticism toward small companies and the complexity of NBY’s pipeline may explain the limited investor interest. The first question asked by many investors is how can a company with the limited financial resources of NovaBay have such a broad, late stage pipeline? Something must be amiss.
There is a good explanation for the broad pipeline as the products being developed for impetigo; viral conjunctivitis and urinary encrustation are all based on different formulations of the same molecule. In addition, each of these is an infectious disease indication whose endpoints can be more quickly reached and at lesser development expense than drugs targeted at chronic diseases. Moreover, partnering deals with Galderma and Alcon have funded much of the early development costs in impetigo and viral conjunctivitis.
Perspective on NovaBay’s Technology Platform and Its Products
Over hundreds of millions of years, the immune system has evolved to defend humans from the non-stop attack of pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, fungi and yeast which see the human body as a luxuriant feeding ground. Exponential growth in understanding the functioning of the human immune system is leading to the development of new and novel therapeutic advances. One of the most promising research approaches in biotechnology is immunotherapy and NovaBay is a leading participant.
NBY’s technology base stems from an understanding of the action of neutrophils in the body. The first line of defense against pathogens is the barrier formed by skin and mucous tissue. When a pathogen breaches this barrier and causes an infection, the immune system springs into play and the first immune cell encountered by the pathogen is usually a white blood cell called a neutrophil. The neutrophil surrounds and ingests the pathogen and also produces chemicals that act to kill the pathogen and inactivate toxins produced by it. Unlike antibiotics and other anti-microbial agents developed by man, pathogens have not been able to evolve resistance to the mode of action used by neutrophils.
The technology base of NovaBay is based on an understanding of toxic molecules that neutrophils produce to kill bacteria and inactivate their toxins. It is specifically focused on hypochlorous acid (HOCl) and its derivative molecules, N-chlorotaurine (NCT) and N,N-dichlorotaurine (NNDCT). In their natural state, all three of these molecules are very short lived so that they must be delivered by the neutrophil to the site of the infection; they are not candidates for drugs. NovaBay has discovered how to stabilize these molecules allowing for their use in drugs that can be delivered topically as solutions and gels for the treatment of diseases caused by infectious pathogens.
The key product for NovaBay is NVC-422 which is a stabilized form of NNDCT. This molecule is actually the basis of three distinct drugs as it is being developed for dermatological applications as a gel formulation, as an eye drop for adenoviral conjunctivitis and as a liquid instillate for treating urinary catheter encrustation and blockade. NeutroPhase is a stabilized form of hypochlorous acid.
NVC-422 in Impetigo
What Is Impetigo?
Impetigo is a highly contagious bacterial skin infection that is common in pre-school children and adolescents participating in contact sports such as football and wrestling; it is less common in adults. Bullous impetigo primarily affects children under two years of age causing blisters on the trunk, arms and legs. The skin around the blister is usually red and itchy but not particularly sore. The blisters break and scab over with a yellow-colored crust that can last for several days. Infectious impetigo is a more serious form of the disease in which the infection penetrates deeper into the skin’s second layer, the dermis. It is characterized by painful, pus-filled sores that can turn into deep ulcers in the legs and feet.
Impetigo is primarily caused by Staphylococcus aureus and occasionally by Streptococcus pyogenes. Mild cases are treated with washing and cleansing the lesions and the applications of antiseptics and topical antibiotics such as Bactroban (mupirocin). When topical agents fail or there is a large area of skin involvement, oral antibiotics such as penicillins, cephalosporins and erythromycin may be added. MRSA as a causative agent for impetigo is a growing concern.
Results for NVC-422 in a Prior Trial Was Encouraging
NovaBay conducted a phase II proof of concept trial in impetigo in July, 2010. The study enrolled 129 children, aged two to eleven, at two centers in the Dominican Republic. It used three different, ascending doses of NVC-422 given in a gel for a treatment period of seven days. Patients and physicians were blinded to which dose was administered, but there was no control group.
Children entered into the study had to show a gram positive stain that indicated that the infection was caused by Staphylococcus or Streptococcus. A sample of the exudate or pus was taken from a target lesion on the first day of treatment and then cultured in a laboratory to determine the bacterium causing the infection. Bacteriological success was defined as the absence of that bacterium at day 8 or day 15 based on a culture of exudate from the target lesion or no exudate material available for extraction from the target lesion.
A paper was presented at the October 2010 ICAAC meeting in which the authors presented their observations and conclusions as follows:
- The clinical response rates at days 8 and 15 for all three doses was higher than 84% which the author of the study compared to historical response rates of 30% to 50% seen in the placebo groups of other studies.
- 10 out of 10 MRSA infections were resolved at day 8.
- There were 103 patients with a clinical cure who were evaluated at days 8 and 15. There were no recurrences of impetigo in any of these patients between days 8 and 15.
- Bacteriological responses (inability to detect bacteria) at days 8 and 15 were 87% or greater, just slightly better than the 84% clinical response rate.
- Adverse events occurred in 7 of the 129 patients enrolled in the study. They were predominately mild to moderate reactions at the application site and all adverse events resolved at the end of treatment.
- 96% of subjects enrolled completed the study in accordance with protocols at day 8 and 82% returned for the follow-up at day 15.
NVC-422 Is Partnered with the Swiss Company Galderma for Dermatological Diseases
In March 2009, NovaBay partnered NVC-422 with Galderma, headquartered in Lausanne, Switzerland with operations in the EU, US, Canada and Brazil to develop NVC-422 in dermatological conditions including impetigo and acne. This company is the largest prescription dermatological company in the world.
Galderma has exclusive worldwide rights and will pay royalties that start at 10% and escalate with sales to a maximum level of 30%. Galderma will conduct and pay for all of the clinical trials in impetigo and acne. NovaBay has retained all rights to co-promote the products developed under the agreement in hospitals and other healthcare institutions in North America.
Galderma has just begun a worldwide phase IIb/III study that will enroll 350 impetigo patients. Treatment will last for 7 days and an evaluation of treatment will be made on days 7 and 15 after treatment begins. The study should be completed in 2Q, 2013 with topline data available in 3Q, 2013. The study is powered as a pivotal study, but it is highly probable that the FDA will require a second confirmatory study for approval. This second trial could start in 4Q, 2013 and finish in 2H, 2014. A filing could be made in 2015 leading to approval and a US launch in 2016.
The phase IIb/III trial will divide the 350 enrolled patients evenly among a BID and TID dose of NVC-422 and placebo. In the phase II trial of NVC-422 in 120 patients, it was effective in 92% of impetigo patients at the highest and most effective dose. This study was not placebo controlled, but other studies in impetigo have shown about 30% to 50% effectiveness in the placebo group. If these effectiveness rates are approximated in the ongoing trial, NVC-422 should show strong statistical significance in efficacy over placebo.
The Market Opportunity
Galderma has said that it sees impetigo as a potential $400 million worldwide sales opportunity. NovaBay conducted a market survey of 150 physicians asking them to list the most important attributes they would like in a new product for impetigo. The two items at the top of their list were preventing the emergence of resistant bacteria and effectiveness against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus or MRSA. NVC-422 has demonstrated in pre-clinical passage studies that resistant bacteria do not emerge to NVC-422. In the phase II trial in impetigo, NVC-422 clinically cured 10 out of 10 patients who had impetigo caused by MRSA. These two product characteristics argue for a quick uptake following commercialization if this trial replicates results in the earlier phase II proof of concept trial.
The rapid growth of MRSA infections presents a problem for the initial physician treating the disease who is likely to be a pediatrician or general practitioner. Non-resistant staphylococcus infections respond readily to available topical antibiotics, but MRSA infections often don’t. If untreated, they have the potential to become dangerous and potentially life threatening. It takes several days to culture the bacterium and determine if it is resistant. Hence the physician initially is treating empirically and a new product like NVC-422 with efficacy against both MRSA and non-MRSA infections would be the logical choice for empirical treatment.
The estimated global market for impetigo is shown in the next table.Impetigo is a gateway indication for other dermatological diseases such as acne. NVC-422 may also find applications in surgical settings and wound treatment. It would also likely be used in combination with systemic drugs. There is the potential for very significant sales outside of the impetigo market.
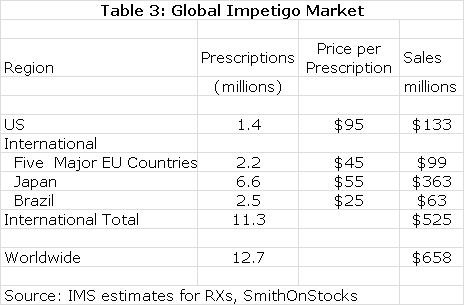
European and Brazilian approval could follow the same timeline as the US while Japan might require trials in Japanese patients that could delay approval until 2017. The product characteristics of NVC-422 argue for significant market penetration. In my model, I have assumed that peak market share is reached in each market six years following introduction and that peak shares are as follows: US (45%), Europe (35%), Japan (25%) and Brazil (35%). I also assume that NVC-422 is priced at parity to existing products in these markets.
Galderma will pay an escalating royalty on sales that I estimate to start at 10% and to reach 30% on sales above $300 million. A summary of my sales and royalty projections are shown for 2016 through 2020and for 2028. In 2028, the patent coverage expires and I am assuming no sales beyond 2028.
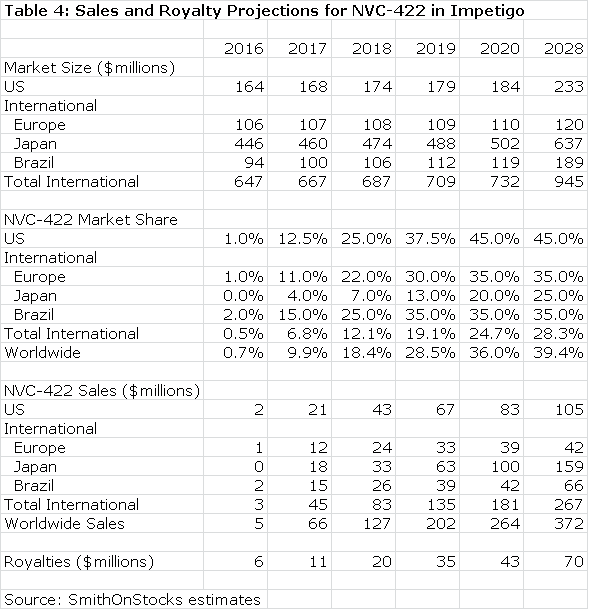
Galderma has estimated that the use of NVC-422 to treat impetigo could be a $400 million worldwide sales opportunity, but hasn’t specified the point in time at which these sales might be reached. Against this, my projection of $253 million in sales in 2020 appears reasonable or somewhat conservative. Moreover, success in treating impetigo could give rise to off label use in other dermatological conditions such as acne and in surgical settings and wound healing. I have not included any estimates for sales in these indications, which adds another layer of conservatism to my estimates.
Value of NVC-422 in Impetigo
Based on the available clinical data and the validation provided by the Galderma partnership, I believe that the chances for success are good in the impetigo indication. This alone would make NovaBay is an attractive investment. The royalty stream for the period 2016 through 2028 can be discounted to arrive at a net present value. Using a discount rate of 10%, the net present pretax value of the royalty stream is $118million which compares to the current market capitalization of $37 million. Using a discount rate of 15% produces a net present pretax value of $70 million.
Use of NVC-422 for Treating Adenoviral Conjunctivitis
What Is Conjunctivitis?
Conjunctivitis is an infection of the conjunctiva, the membrane that lines the whites of the eye and the inner eyelids. It is about equally caused by bacteria and certain serotypes (variations) of the adenovirus family. More commonly known as pink eye, conjunctivitis usually starts in one eye as watering, itching and irritation. Most cases resolve on their own using only treatments that rinse and cleanse the eye.
Bacterial conjunctivitis can be treated with antibiotic eye drops, but there is no approved treatment for adenoviral conjunctivitis. Physicians do not have the time or capability to conduct the tests needed to accurately determine whether the infection is caused by bacteria or adenovirus so they must treat empirically based on their clinical judgment. As a consequence, adenoviral conjunctivitis is often mistakenly treated with antibiotics which are ineffective.
Conjunctivitis sometimes involves the cornea; the transparent membrane that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber of the eye. Adenoviral infections involving the cornea are a more severe type of infection that is called epidemic keratoconjunctivitis or EKC. Symptoms include red eye, blurred vision, tearing, discharge, eyelash matting or crusting and the sensation of a foreign body in the eye. EKC is highly contagious. One eye is usually infected first with the infection spreading to the other eye within two to three days in about 60% of cases. Moreover, half of people in close proximity such as family or sports team members usually become infected.
EKC can result in severe vision impairment in infected patients. In approximately 20-50% of patients, corneal opacities are developed due to sub-epithelial infiltrates (SEIs) which can cause blurred vision. Epidemic keratoconjunctivitis is commonly associated with adenoviral serotypes 8, 19 and sometimes 37.
A Prior Trial of NVC-422 Conducted By Alcon Failed To Achieve the Primary Endpoints
Alcon, a division of Novartis, licensed NCV-422 for use in ophthalmology. It then designed and conducted a trial aimed at gaining approval in adenoviral conjunctivitis. The presumed mode of action of NVC-422 suggests that it would be effective in conjunctivitis whether caused by bacteria or adenoviruses. However, the great unmet medical need is for a treatment for adenoviral conjunctivitis and running a trial designed to show efficacy for all types of conjunctivitis would have been prohibitively large and complex.
The trial that Alcon designed allowed physicians to enter all patients that they clinically diagnosed as having adenoviral conjunctivitis. After the patients were enrolled, precise PCR technology was used to determine if patients actually had adenoviral infections and the serotype causing it. The study was planned to identify and evaluate 220 patients with confirmed adenoviral infection.
After enrolling 452 patients, an interim analysis showed that only 81 patients (42 on NVC-422 and 39 on control) had adenoviral infections confirmed by PCR. The primary endpoint of the trial was to show a 20% difference between NVC-422 and control in eradication of adenovirus at day 18 after treatment. The trial showed only a 7% difference and did not meet its primary endpoint. Alcon ended the trial and shortly afterwards returned the product to NovaBay.
NovaBay is Conducting a New Trial on Its Own
Experienced biotechnology investors have seen that the failure of a clinical trial does not always spell the end of a drug. Sometimes, careful analysis of the trial data will point out flaws in the trial design and identify subsets of patients who benefited from the treatment. This can lead to the design of a new trial with a reasonable chance of success.
NovaBay’s analysis of the 81 patients with adenoviral infections in the Alcon trial revealed that 30 had EKC. In this subgroup there was a 15% difference in viral eradication at day 18, which was close to the 20% proscribed endpoint. In addition, 92% of EKC patients treated with NVC-422 reported resolution of blurred vision versus 50% in the control group and 60% of NVC-422 patients experienced resolution of SEIs versus only 30% on control. These were encouraging findings as EKC is the condition that is most likely to result in severe damage to the vision of infected patients, and is of primary concern to the ophthalmology community.
Based on these findings, NovaBay decided to go forward with a second trial, which began enrollment in May 2012. This is designed to enroll 450 patients in the US, India and Brazil. One important difference in this second trial is that patients entering must be confirmed as having adenoviral conjunctivitis through a test that takes about ten minutes to perform. This diagnosis must later be confirmed by a more precise PCR test, but it should result in almost all enrolled patients having adenoviral infections as opposed to only 18% in the Alcon trial.
This second trial is also designed to show that NVC-422 is effective against those serotypes that cause EKC and the goal is to get this included in the package insert. In actual clinical practice, physicians will not know if they are treating adenoviral conjunctivitis caused by serotypes that lead to EKC or for that matter if the infections are caused by bacteria or adenovirus. They will elect to treat empirically and in order to make sure that they are covering all possibilities they will probably use a combination of a drug approved for bacterial conjunctivitis and NVC-422 to make sure that they cover EKC.
Enrollment for the new phase II trial called BAYnovation started in May of 2012 and could complete in mid-2013. Topline results from the trial could be released in 3Q, 2013. If the results are positive, this trial could be considered a pivotal trial, but the FDA will almost certainly require a second confirmatory trial. Assuming timelines similar to the first trial, results from the second trial could be available and an NDA filing made in 2H, 2014. Again assuming success in the second trial, NVC-422 could be approved and marketed in 2016.
The Market Opportunity in Conjunctivitis
The addressable market for NVC-422 in conjunctivitis could be huge although current data on the size of the market is sketchy. If efficacy against EKC is established in the current trial, it would be particularly important. Because conjunctivitis is a disease that resolves most often on its own, it is not a reportable disease to the CDC and this also prevents reporting of EKC, which often requires treatment.
In Japan, EKC is considered a reportable disease and there are 1 million cases recorded annually. Extrapolating this incidence to the US, suggests that there could be as many as 3.7 million cases in the US. Because of the epidemic nature of EKC, an infection in one member of a family could lead to other members of the family being treated resulting in a multiplier effect on the first prescription. The same reasoning applies to military personnel, sports and other activities in which there is close physical contact.
Estimates on the size of the global market for conjunctivitis are shown in the following table:
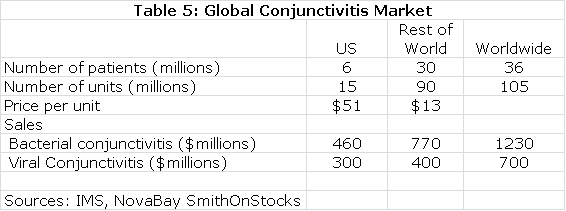
The next table summarizes my sales and royalty projections for the US and International markets. It is probable that there will be enough patients treated in the Brazilian segment of the phase IIb/III trial to allow for regulatory submission based on just one trial and this could lead to a launch and an estimated $5 million of sales in Brazilin 2015. I think that Japan will require trials in Japanese patients that would result in commercialization in 2017. In the US, Europe and all other markets, I am assuming launches in 2016. This, of course, assumes success in the clinical trials.
Because there are no approved products for viral conjunctivitis, I think that there would be rapid penetration in both the US and international markets. I also would expect NVC-422 to be used widely for treating conjunctivitis as there is no easy way to determine whether the infection is viral or bacterial and NVC-422is probably effective in both.
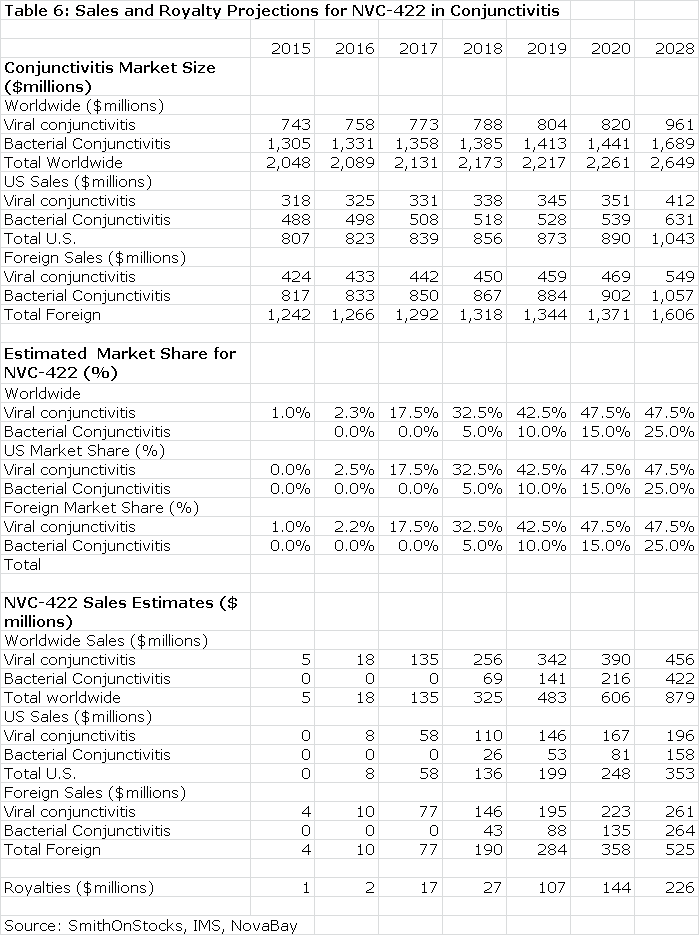
The Value of NVC-422 Used to Treat Conjunctivitis
Table 6 assumes that NVC-422 will be partnered in both the US and international markets. Currently, NovaBay controls all worldwide rights. I estimate that the royalty rate will be comparable to that paid by Galderma for the impetigo indication; it starts at 10% and escalates to 30% on sales above $300 million.
The royalty stream for the period 2016 through 2028 can be discounted to arrive at a net present value. Using a discount rate of 10%, the net present pretax value of the royalty stream is $786 million which compares to the current market capitalization of $37 million. Using a discount rate of 15% produces a net present pretax value of $530 million.
Use of NVC-422 for Encrustation and Blockage of Urinary Catheters
Urinary Catheters Can Become Encrusted and Blocked by Bacterial Colonies
In some disease conditions, neurological disorders interfere with the ability to void urine from the bladder. This is treated by inserting a catheter through the urethra and into the bladder. Urine then drains through the catheter into a collection bag. The most commonly used device is the Foley catheter. It has one tube that empties urine and a second with a balloon at its end through which saline is instilled to inflate the balloon and hold the catheter in place in the bladder.
A major problem with catheter use is that it provides easy access for bacteria to migrate upwards from skin and external surfaces into the bladder. Also, the retention balloon of the Foley catheter creates stagnant urine pools around it in the bladder. This provides bacteria a luxuriant environment for growth so that in a matter of a few hours, rapid replication can result in millions of bacteria.
Bacteria are very good at adhering to catheter surfaces as they flow by in the urine. Once attached, they multiply very rapidly and some species cover themselves with a protecting gel or biofilm. This enhances the formation of large colonies that can contain as many as one billion bacteria per centimeter of catheter. Biofilms are difficult to treat with antibiotics and are the primary cause of urinary encrustation and blockage or UCBE; eliminating or reducing the size of UCBE is the primary therapeutic goal of NVC-422.
In addition to blocking the catheter, UCBE can also lead to catheter associated urinary tract infections or CAUTI. The current standard of care is irrigating solutions that try to clear UCBE, but don’t have anti-bacterial effects against CAUTI. Attempts to treat UCBE by giving antibiotics prophylactically or by using antiseptic coated catheters have not been shown to decrease UCBE.
Who Is At Risk of UCBE
It is estimated that there are over 335,000 patients in the US that have permanently implanted catheters who are susceptible to UCBE and that approximately 100,000 of these patients are chronically affected. UCBE can lead to urine being blocked in the bladder and causing it to extend. If the catheter is not replaced, the urine can back-up into the kidney and cause an infection.
Patients most at risk for UCBE come from diverse conditions that cause neurological damage such as spinal cord injury, stroke, multiple sclerosis or just old age. It is a large and diverse group ranging from young paraplegics who have suffered a sports injury to immobile bed ridden elderly men and women.
Results from InVitro and Early Human Phase II Clinical Studies
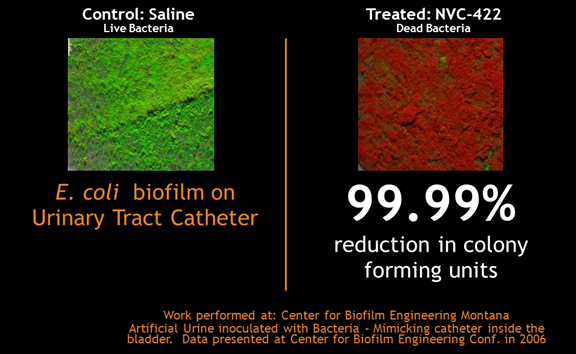
In vitro studies with NVC-422 have shown that it is capable of penetrating a biofilm and effectively killing the contained microbes. With anti-bacterial agents, efficacy in laboratory models is a good predictor that the drug will be effective in humans if it can be delivered to the site of the bacterial infection. NVC-422 is instilled through the urinary catheter into the bladder and then drained using a proven technique for delivering antibiotics. The therapeutic goal is to keep the bladder and catheter substantially free of bacteria and biofilm, treating or preventing both UCBE and CAUTI.
NovaBay has begun a three part phase II trial to determine if NVC-422 can safely clear or reduce the size of UCBE in chronically catheterized subjects. The design for part one of the study called for patients to be given either NVC-422 or an irrigating solution for three days a week-Monday, Wednesday and Friday- for two successive weeks. They were then given a washout period without either NVC-422 or control and switched to the other treatment. This is called a cross over study in which it can be determined how each patient fares on NVC-422 as compared to standard of care irrigating solutions. Patients in the study form both the control and active drug group.
The current standard of care for treating urinary catheter blockage and encrustation requires catheter irrigation three times daily or 21 times per week. The primary goals of NovaBay’s phase 2 trial are to show that it is safe and can reduce treatment to three or possibly two times per week from 21 required with standard of care. It is not designed to address the effect of NVC-422 on bacterial infections, which would require a much more extensive and lengthy trial.
The first part of the phase II trial enrolled 20 patients with encouraging results. However, a two week study is not sufficient time to demonstrate meaningful efficacy. Investigators found that some of the saline patients were experiencing catheter blockage and in those patients who incurred catheter blockage while on standard of care, NVC-422 prevented blockage in 80% of those patients. The results in part one encouraged the company to move on to part 2 with a new more potent formulation and somewhat different study design.
This second part of the phase II study is underway and has enrolled over 20 patients with top-line results expected in Q1, 2013. The study design is similar to part one, but will use a more potent formulation of NVC-422. The outcome measures of part 2 are more refined than in part 1; one will be catheter patency following treatment as determined by the increase in non-encrusted cross sectional area at pre-selected loci on the catheter. A secondary outcome measure will be incidence of catheter blockage requiring early removal. Catheters removed prior to completion of the treatment regimen will be assessed for biofilm using both qualitative and quantitative measurements. These are much more informative endpoints than those for part one of the trial just completed. If results are positive, NovaBay will also open part three of the study using a more potent formulation with the goal of reducing treatment from three times per week to two.
Current Treatment
The current irrigating solutions used to treat UCBE are based on saline or mildly acidic solutions such as vinegar. There is an approved drug on the market called Renacidin that is a citric acid solution. It was approved as an orphan drug for bladder and kidney stone patients. Citric acid dissolves the calcium which is the main structural element of UCBE and also kidney and bladder stones, but has no anti-bacterial effect. These solutions require two to three rinses per day. The patient just can’t easily comply with this and even home health nurses often only rinse the catheter once per day. The sharply reduced number of rinsings required with NVC-422 is a major commercial advantage.
Regulatory Pathway Might Lead Down the Device Trail
The phase II trials are designed to show reduction or clearance of UCBE and not an anti-bacterial effect as such trials would require much more time and complexity. This may lead NovaBay to file for FDA approval as a device and not a drug with a claim for catheter patency, a much simpler 510-K process; they have not yet discussed this approach with the FDA. Filing requirements for a 510-K are much reduced and review time can be much quicker.
There is some possibility if the FDA considers NVC-422 as a device and not a drug that the data from part two of the phase II study could be the basis for approval. This could lead to approval in early 2014. If required, they could enroll another 20 patients to confirm these results by the end of 2013 and approval might be gained in late 2014. This is a very optimistic scenario. I am projecting that the product will be developed via the NDA route and will reach the US market in 2017.
The Market Opportunity
It is estimated that over 335,000 permanently catheterized U.S. patients are susceptible to UCBE and approximately 100,000 of these chronically suffer from this condition. There is no effective therapy; most current products are irrigating solutions that break up blockage. The principal bacteria causing UCBE is Proteus mirabilis; NVC-422 is effective against this agent and offers the potential to eradicate the causative agent in UCBE as well as breaking up the blockage in an irrigating solution. It addresses a great unmet need.
The immediate value proposition for NVC-422 lies in the reduced attention needed for catheter patency. It may require only 2 catheter irrigations per week versus three times per day that is suggested for standard of care. There are other advantages that may accrue from its anti-bacterial effect, but these require longer term studies to evaluate. NovaBay did a survey of 150 physicians to determine that they thought might be a reasonable price. The survey indicated that NovaBay could charge $15 per use for NVC-422 based only on the reduced number of irrigations required.
I have made some projections for the opportunity in UCBE in the US. I estimate that there are currently 100,000 long term catheter use patients who experience chronic UCBE that will require twice a week treatment and another 235,000 who experience less frequent blockage who will require twice a month treatment. This is based on findings in the NovaBay survey. I further estimate that population growth is 2% annually and that each treatment will be priced at $15. This allows for the calculation of the addressable market. I look for good penetration in the 100,000 chronic UCBE patients of 60% and a lesser 15% in the prophylactic population of 235,000. This is shown in the next table.
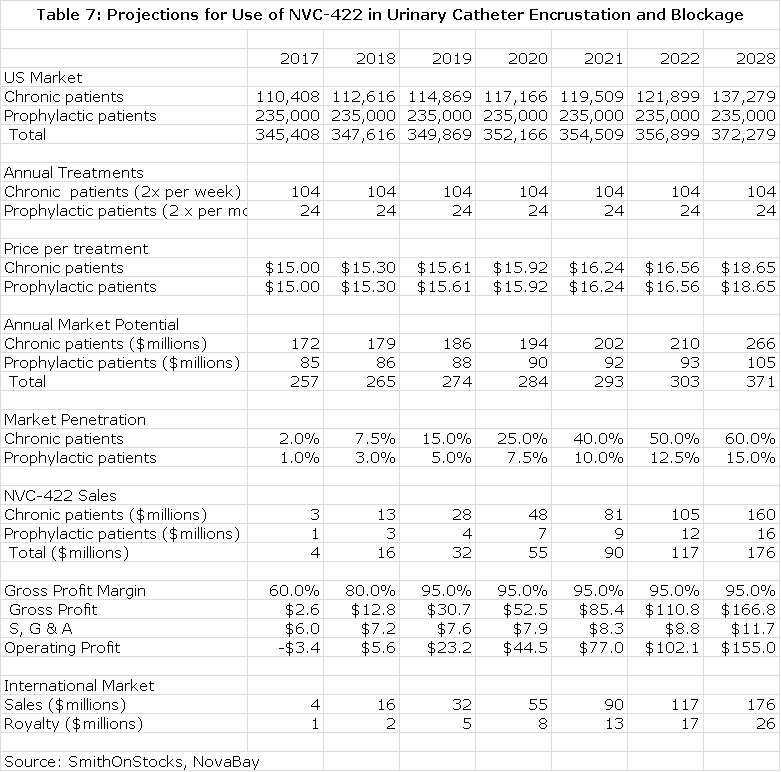
Value of NVC-422 in Urinary Catheterization Encrustation and Blockade
I project that NovaBay will form its own sales force to market the product in the US. About 80% of potential sales are concentrated in 50 clinical sites so that a small sales force of 20 salesmen could reach most of the market. The cost per salesman would be about $200,000 and the gross margin would be about 95% at peak sales. This allows for the calculation of operating income. Discounting this stream of operating profits at a 10% discount rate results in a net present pretax value of $499 million and at a 15% discount rate it would have a net present pretax value of $353million.
I assume that international sales will reach the same level as US sales and that the product will be partnered at a royalty rate of 15%. Discounting the resultant royalty stream at 10% results in a net present pretax value of $89 million and at a 15% discount rate is $63 million.
NeutroPhase® Wound Cleanser
What NeutroPhase Is Used For
NeutroPhase is a proprietary wound cleansing solution containing hypochlorous acid or HOCl. FDA has approved it through the 510(k) process for dermal wound cleansing. It is indicated for moistening absorbent wound dressings and cleaning minor cuts, minor burns, superficial abrasions and minor irritations of the skin. It is also intended for moistening and debriding acute and chronic dermal lesions, such as Stage I - IV pressure ulcers, stasis ulcers, leg ulcers, diabetic foot ulcers, post-surgical wounds, first and second degree burns, abrasions and minor irritations of the skin.
The first step in the treatment of a chronic wound is to cleanse the wound bed. This can be achieved in a number of ways, but in all cases some form of a wound cleanser or wash is used. The majority of 510k cleared wound cleansers on the market today have drawbacks. These include cytotoxicity (killing of cells), ineffective antimicrobial activity or short shelf life. NeutroPhase probably has advantages over existing agents in terms of potency and shelf life, but this has not yet been established in clinical trials.
NovaBay’s formulation is a shelf- stable form of hypochlorous acid or HOCI. It is a solution of pure HOCl in saline with effective concentration of 0.01%. Pure HOCl is 500 times more powerful than NaOCl which is often found in competing products. Currently data supports a shelf life of 12 months, but stability studies are ongoing to further extend shelf life.
Market Opportunity
NeutroPhase has been approved via the 505-b-2 regulatory route and could be marketed in the US in 1Q, 2013. NovaBay’s strategy is to manufacture the product in the US and supply it at a transfer price to partners in the US and abroad. The company has announced a partnership with Pioneer Pharma for distribution in China and Southeast Asia. It is negotiating other deals in the US, Europe and other areas of the world. A US partnership could be announced in Q1, 2013.
Although NeutroPhase is a very good product, physicians are generally satisfied with existing products and the potential is limited in the US and other markets, at least in the near term. My assumptions for sales by region are as follows:
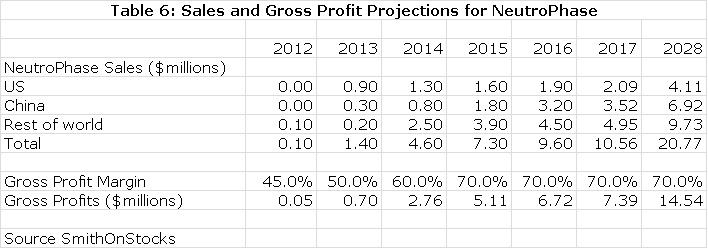
Value of NeutroPhase
My projections suggest slow, but steady progression in the next few years as shown in the previous table. I have also projected a gross margin on the transfer price that allows me to calculate what roughly amounts to a royalty stream. Discounting this stream at a 10% discount rate results in a net present pretax value of $54 million; a 15% discount rate results in $36 million net present pretax value.
In writing this report, I first did an in-depth study of each of the products. This work is included in the appendix for those readers who wish to go into more detail.
Appendix
NovaBay’s Core Technology
The body’s primary defense against infection is the anatomic barrier of the skin and mucous membranes. Once pathogens penetrate this barrier, the next line of defense is the white blood cells of the innate and adaptive immune system, the most numerous of which are the neutrophils; they constantly patrol the blood stream and are almost always the first white blood cell that a pathogen encounters. When a neutrophil encounters a bacterium or other pathogen, it engulfs and ingests it in a process known as phagocytosis.
Neutrophil phagocytosis of pathogens produces large quantities of superoxide, a reactive oxygen species. Superoxide through enzymatic action is converted to hydrogen peroxide and then hypochlorous acid (HOCl) which has potent antimicrobial activity.
Excess HOCl reacts with the amino acid taurine to form N-chlorotaurine (NCT), which in turn is further chlorinated to produce N,N -dichlorotaurine (NNDCT); both are potent antimicrobial agents that act by direct oxidation of sulfhydryl moieties exposed on surfaces of pathogens, hence rendering microbes inactive without creating resistance. This biological process is presented pictorially below:

(a) Myeloperoxidase (MPO) generates HOCl which can attack the bacterium directly. (b) HOCl can also react with taurine to form NCT, which can also attack the bacterium. (c) HOCl can further react with NCT to form NNDCT, which also attacks the bacterium. (d) All three compounds bombard the bacterium until the bacterium dies.
NovaBay has two approaches to commercializing these three potent, yet unstable, anti-microbial compounds. The commercialization of stable and pure HOCl has been accomplished with NeutroPhase® (see discussion later in this paper). The second approach is to synthesize stable analogs of NCT and NNDCT that retain their antimicrobial properties.
NCT and NNDCT have been effective without the emergence of resistant pathogens that invariably arise against antibiotics, anti-viral and anti-fungal drugs. However, both have very short half-lives and are only effective when delivered on demand by neutrophils. NovaBay has chemically modified these chlorotaurine compounds so that, unlike their naturally occurring counterparts, they have excellent stability in solution while retaining the anti-microbial potency. NovaBay has numerous composition of matter patents relating to multiple analogs of the chlorotaurines.
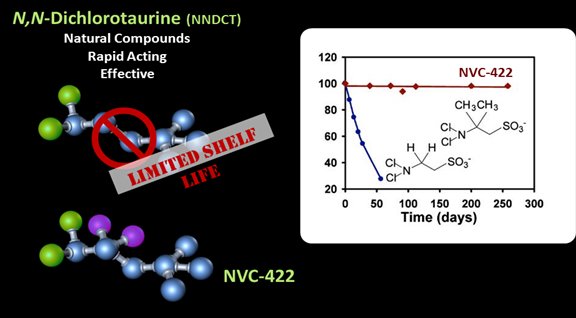
NovaBay’s lead drug, NVC-422, retains the biological activity, safety profile, and most of the physiochemical properties of NNDCT. Importantly, through the chemical modifications to NNDCT, NVC-422 is chemically stable both in pure form and in solution, making it a viable therapeutic agent that is: (1) fast acting, (2) broad in spectrum of activity, (3) effective against multi-drug resistant bacteria, (4) effective against biofilm, (5) has a good safety profile and (6) has a low propensity for the development of resistance.
Unlike most drugs, a good insight into the property of anti-microbials can be determined from in vitro(in culture dishes in a laboratory) and disease models in animal studies. NVC-422 has killed in vitro all bacteria, viruses, yeasts and fungi against which it has been tested, notably the multi-drug resistant bacteria including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE). It has a quick onset of action that can kill bacteria in minutes as opposed to hours for antibiotics, is effective against biofilm and has shown a good safety profile.
NVC-422 in Urology
The Use of Urinary Catheters in Urology
In urinary catheterization, a latex, polyurethane, or silicone tube (the urinary catheter) is inserted through the urethra or through the skin above the pubis bone into the patient’s bladder in order to allow the urine to drain from the bladder for collection in a bag. The most commonly used is the Foley catheter. After insertion into the bladder, the balloon is inflated with sterile water to keep it from slipping out. Patients may remain on a Foley catheter for a day or weeks and in some cases on a long term basis.
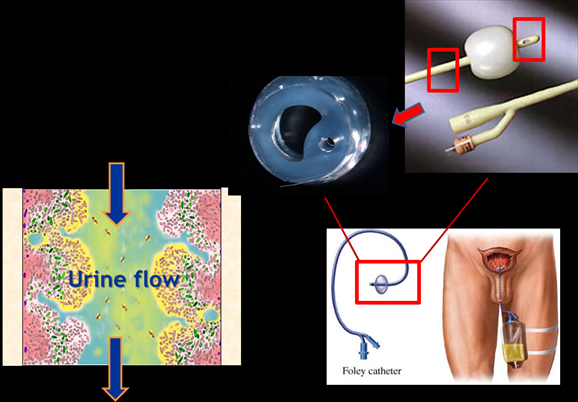
A major problem with catheter use is that it provides an easy way for bacteria to migrate upwards from contaminated skin and external surfaces through the catheter and into the bladder. The mere presence of the catheter in the bladder also undermines an important defense mechanism against bacteria. The bladder normally fills and empties urine and in the process eliminates bacteria; this extension and contraction doesn’t occur with the continual drainage resulting from catheterization. Also, the retention balloon of the Foley catheter in the bladder creates stagnant urine pools around it. Bacteria migrating up the catheter find themselves soaked in an excellent environment for bacterial growth and in a matter of a few hours; millions of bacteria can fill the urine.
Urinary Catheter Encrustation and Blockage (UCBE)
Bacteria are very good as sticking to surfaces rather than swimming around in urine allowing them to adhere to catheter surfaces as the urine flows around them. Once attached they multiply very rapidly and some cover themselves with a protecting gel or biofilm that results in the formation of large colonies that can contain as many as one billion bacteria per centimeter of catheter. Biofilms are difficult to treat with antibiotics and are the primary cause of urinary encrustation and blockage (UCBE).
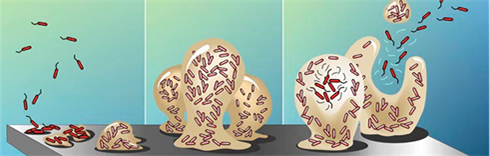
The crystalline biofilms are primarily caused by urease-producing bacteria. Urease raises urinary pH and results in the formation of calcium phosphate and magnesium phosphate crystals which become encrusted in the developing biofilm. These encrustations can grow rapidly and impede or block the flow of urine. Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris and Providencia rettgeri are the urease producing bacteria species that are most capable of creating highly alkaline urine that lead to biofilm formation; they are the root cause of UCBE. Morganella morganii and Staphylococcus aureus cause some crystal deposition in their biofilms but usually don’t block catheters. UCBE can be caused by as many as six different microorganisms but Proteus is the most frequent cause.
UCBE can lead to severe urinary tract infections and also requires frequent catheter changes. In long term catheterization, there are no current bladder irrigation solutions that can reduce or eliminate CAUTI by keeping the bladder and catheter substantially free of bacteria and biofilm. Antibiotics given prophylactically have not been shown to decrease UCBE nor have antiseptic coated catheters.
Patients at Risk and Market Size
It is estimated that over 335,000 permanently catheterized U.S. patients are susceptible to UCBE and approximately 100,000 of these chronically suffer from this condition. Patients most at risk for UCBE come from such diverse conditions as neurological damage, spinal cord injury, stroke, multiple sclerosis or old age. It is a large and diverse group ranging from young paraplegics who have suffered a sports injury to immobile bed ridden elderly men and women.
About 40% to 50% of long term catheterized patients will experience encrustation and blockage. This can lead to urine being blocked in the bladder causing it to extend. If the catheter is not replaced, the urine can reflux into the kidney causing pyelonephritis and potentially bacteremia.
A study done in nursing home patients in Ohio identified a population of long term catheterized patients and matched them to a control matched for age, gender and health status of a similar number. This study suggested that long term catheters are used with 5% to 10% of patients. There are about 1.5 million nursing home patients in the US so that this would translate into 75,000 to 150,000 patients. The study found that patients on catheters were three times as likely to be receiving antibiotics, to be hospitalized, and to be dead.
Rationale for NVC-422
NVC-422 is instilled into the bladder through the urinary catheter and then drained, using a proven technique that has long been used to deliver antibiotics. . This approach is currently the only therapy that has the potential to reduce morbidity and mortality by killing the pathogens responsible for the formation of UCBE without giving rise to bacterial resistance.
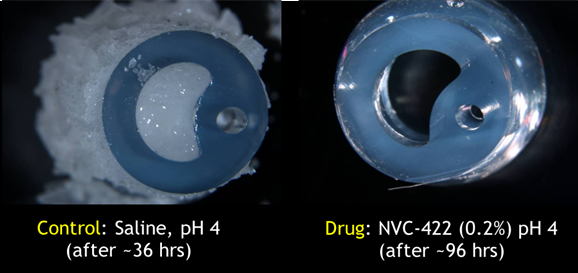
Laboratory model of a human bladder tested intentional biofilm creation and eradication.
A bladder instillation solution that can keep the bladder and catheter substantially free of bacteria and biofilm is expected to provide a practical and cost-effective means of minimizing CAUTIs. In-vitro studies with NVC-422 have also shown that it is capable of penetrating a biofilm and effectively killing the contained microbes. NovaBay’s goal is to market this product in the United States and to seek a partner outside the US.
Phase II Study Design
The phase II trial now underway is intended to evaluate the safety and antimicrobial effects of NVC-422 on bacteriuriain chronically catheterized subjects. The trial is enrolling male and female patients that require chronic indwelling transurethral or suprapubic urinary catheters and have a recent repeated history of urinary catheter encrustation and/or blockage. The study is a double-blinded, placebo-controlled, crossover design. Patients’ catheters are irrigated with a solution of NVC-422 or placebo every other day excluding weekends for two weeks resulting in seven treatments over two weeks. This is then followed by a one to three week washout period. After this, placebo patients are switched to the NVC-422 solution and vice versa.
To be included, patients have to have a chronic indwelling transurethral or suprapubic urinary catheter and have a recent repeated history of urinary catheter encrustation and/or blockage. The objective of this study is to assess the use of NVC-422 in preventing or reducing urinary catheter encrustation and blockage.
The current standard of care for treating urinary catheter blockage and encrustation (UCBE) requires catheter irrigation three times daily. NovaBay’s phase 2 trial has the goal of showing that an irrigation solution containing NVC-422 can reduce treatment to two or three times per week. Over the course of one week, this would reduce the number of catheter irrigations from 21 to 2 or 3. In addition to clearing the catheter, it is thought that NVC-422 may kill the bacteria responsible for encrustation. If this is so, in addition to reducing the number of catheter changes required, it could: (1) lower the incidence of urinary tract infections, (2) reduce the recurrence of UCBE, (3) improve continence and (4) improve quality of life.
Initial Results of Phase II Trial
The part 1 or first phase of the trial enrolled 20 patients. In the evaluable patients, catheter irrigation with NVC-422 was able to prevent catheter blockage in 80% of the paired comparisons in which complete catheter blockage occurred during the treatment period. The results in part 1 encouraged the company to move on to part 2 with a new more potent formulation and somewhat different study design.
NovaBay is testing a more potent formulation of NVC-422, which it hopes will support a more favorable dosing schedule that will reduce the number of required catheter irrigations from the current standard of care of two or three treatments per day to only two or three treatments per week. The study is underway and has enrolled over 20 patients, with top-line results expected in Q1, 2013. The primary outcome measure of Part 2 will be catheter patency following treatment. This will be based on an increase in the cross sectional area that is not encrusted and will be determined at pre-selected loci on the catheter.
The secondary outcome measures will be incidence of catheter blockage requiring early removal. Catheters removed prior to completion of treatment regimen will be assessed for each treatment group to assess the biofilm. Qualitative and quantitative assessment of biofilm of catheter will be determined for all catheters removed.
NovaBay will also be opening Part 3 of the study in which treatments will be reduced from three times per week to two times per week.
NVC-422 in Dermatology
Impetigo
Impetigo is caused primarily by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. It is a highly contagious skin infection that primarily affects children and infants. There is increasing incidence of MRSA infections. The annual incidence in the US is estimated to be 1 million patients each year.
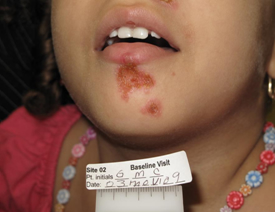
Impetigo is currently treated with topical antibiotics such as Bactroban (mupirocin) or Altabax (retapamulin). Oral antibiotics may be used when topical agents fail or when large areas of skin are involved. Resistance is becoming more of a problem.
Proof of Concept Trial
NovaBay announced encouraging results from a phase II proof of concept trial on July 21, 2010 that investigated the use of NVC-422 in impetigo infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. The study enrolled 129 children, aged two to eleven, at two centers in the Dominican Republic. It looked at three different, ascending doses of NVC-422 given in a gel for a treatment period of seven days. Patients and physicians were blinded to which dose was administered and there was no control group.
The design of the trial called for a patient visit on the first day in which the patient was assessed and, if qualified, treatment was begun. A second visit was required at day 4 for a safety evaluation, a third at day 8 at the end of treatment and a final visit one week later at day 15 to assess clinical and bacteriological responses.
Clinical response was based on the Skin Infection Rating Scale that assesses five symptoms: exudate/pus, crusting, inflammation, itching and pain. Each symptom is assigned a value: 0 for absence, 1 for mild, 2 for moderate and 3 for serious. They are given equal weights and added to form a final score with 15 being the most severe possible rating. Children to be entered into the study had to have ≤ 10 lesions, a SIRS score of ≥4 and to have 3 of the five symptoms present. Clinical success was defined as a SIRS score of 0 for exudate/pus, crusting and pain and a score of 0 or 1 for inflammation and itching. Clinical improvement was considered to be a score of 0 for exudate/pus but not meeting all other criteria. A clinical failure was considered a SIRS score of 1 or greater for exudate/pus.
Children entered into the study also had to show a gram positive stain that indicated that the infection was caused by cocci, which was almost certainly Staphylococcus or Streptococcus. A sample of the exudate or pus was taken from a target lesion on the first day of treatment and then cultured in a laboratory to determine the bacterium causing the infection. Bacteriological success was defined as the absence of that bacterium at day 8 or day 15 based on a culture of exudate from the target lesion or no exudate material available from the target lesion.
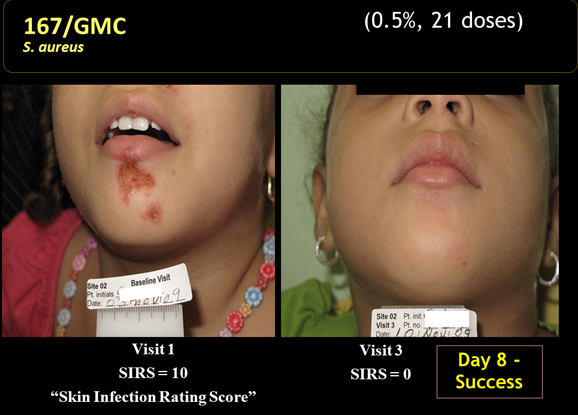
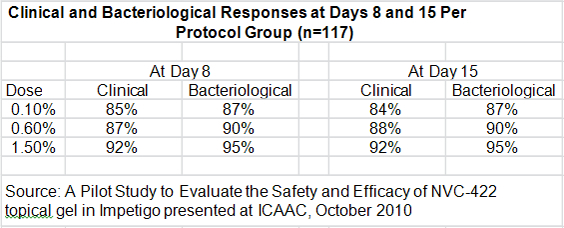
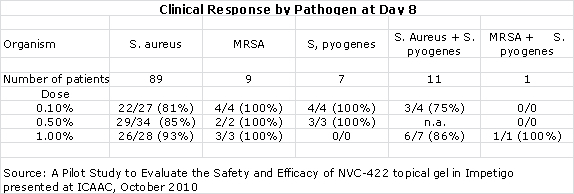
The key discussion points for patients in the per protocol group were:
- The clinical response rates at days 8 and 15 for all three doses was higher than 84% which the author of the study compared to historical response rates of 30% to 50% seen in the placebo groups of other studies.
- 10 out of 10 MRSA infections were resolved at day 8.
- There were 103 patients with a clinical cure who were evaluated at days 8 and 15. There were no recurrences in any of these patients between days 8 and 15.
- Bacteriological responses at days 8 and 15 were 87% or greater, just slightly above better than the clinical response rate.
- There was a modest dose response for the three doses, but it was not statistically significant.
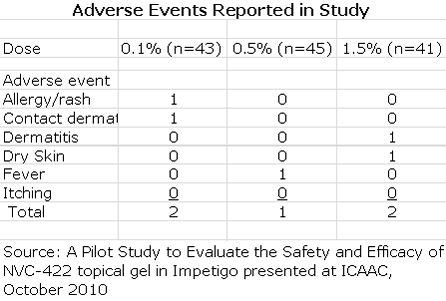
- Adverse events occurred in 7 of the 129 patients enrolled in the study. They were predominately mild to moderate reactions at the application site and all adverse events resolved at the end of treatment.
- 96% of subjects enrolled completed the study in accordance with protocols at day 8 and 82% returned for the follow-up at day 15.
Galderma Relationship and Development Plans
Galderma is one of the largest dermatology focused companies in the world. In March 2009, NovaBay partnered NVC-422 with Galderma for use in dermatological conditions including impetigo and acne. Galderma will pay royalties that start in the low double digits and escalate with sales. NovaBay retained rights to commercialize products for onychomycosis, retains commercialization rights in Asian markets and has an option to co-promote in the institutional markets in North America. Galderma will conduct and pay for all of the clinical trials in impetigo and acne. The agreement was amended in December 2010 and the territory for the impetigo product for Galderma was expanded to worldwide coverage excluding some countries in the Middle East and NovaBay retains the right to co-market products resulting from the agreement in Japan. Additionally, NovaBay has retained all rights to co-promote the products developed under the agreement in hospitals and other healthcare institutions in North America.
The lead indication for Galderma is in impetigo and results from a 300+ patient global phase IIb trial are expected in 1H, 2013. The key differentiating factor for NVC-422 and critical to its commercialization prospects is its potential efficacy against MRSA. In the proof of concept trial, infections resolved in 10 out of 10 patients with MRSA who were treated with NVC-422.
The rapid growth of MRSA infections presents a problem for the initial physician treating the disease who is likely to be a pediatrician or general practitioner. Non-resistant staphylococcus infections respond readily to available topical antibiotics, but MRSA infections often don’t. If untreated, they have the potential to become very dangerous. It takes several days to culture the bacterium and determine if it is resistant. Hence the physician initially is treating empirically and a new product like NVC-422 with efficacy against both MRSA and non-MRSA infections would be the logical choice for empirical treatment.
NCC-422 in Ophthalmology
Adenoviral Conjunctivitis
The conjunctiva is a thin transparent layer that covers the surface of the inner eyelid and the front of the eye. Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the conjunctiva as a result of bacterial or viral infection. The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Keratoconjunctivitis is inflammation of both the conjunctiva and the cornea. Symptoms include red eye, blurred vision, tearing, discharge, eyelash matting or crusting and the sensation of a foreign body in the eye.
Adenovirus is type of virus that has over 64 serotypes or variations. The adeno stems from its first being isolated from the adenoids. Adenoviral caused keratoconjunctivitis is highly contagious and often results in epidemic outbreaks. These are usually referred to as epidemic keratoconjunctivitis or EKC. Epidemic keratoconjunctivitis is commonalty associated with the adenovirus serotypes 8, 19, 37, 54, 56, and 64.
EKCcan cause significant life issues as patients are often advised by physicians not to attend work or school for one to two weeks to avoid spreading the infection when the viruses are rapidly replicating. Approximately 45% of people in a patient’s close surroundings, e.g., family members, will become infected. One eye is usually infected first with the infection spreading to the other eye within two to three days in about 60% of cases with the infection in the first eye being generally more serious.
EKC can result in severe vision impairment in infected patients. Other forms of conjunctivitis tend to resolve themselves over time. They are initially diagnosed and treated by pediatricians and general practitioners in the US. It is EKC that is most troubling and often results in the patient being referred to the ophthalmologist. In approximately 20-50% of these patients, corneal opacities are developed due to sub epithelial infiltrates (SEIs) which can cause blurred vision.

Design and Conduct of First Phase II Safety and Efficacy Trial
NovaBay originally partnered with Alcon to conduct a Phase II proof of concept trial in adenoviral conjunctivitis. It was a double-masked trial conducted by in the US; patients were randomized 1:1 to receive NVC-422 or its vehicle. At the time of enrollment, it can be difficult to distinguish adenoviral conjunctivitis from conjunctivitis caused by bacteria or other viruses. The initial diagnosis was made on the basis of a physicians’ diagnostic checklist or the Adeno Detector Test. The definitive causative agent of the conjunctivitis was identified as adenovirus by using PCR. The study analysis plan defined the primary analysis for those patients with PCR-confirmed adenoviral infections (AITT dataset).
Patients were dosed with one drop per eye eight times a day for 10 days. Microbiological, clinical, and safety evaluations were performed on days 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11 and 18. The primary endpoint was defined as the proportion of patients with sustained microbiological success for eradication of adenoviruses on days 5 and 7. In other words, the virus had to be eradicated by day 5 and or 7 and not return through day 18. Sustained clinical cure was a secondary endpoint. Six different clinical signs and symptoms of the infection were assessed individually. For clinical success, the clinical rating of the signs and symptoms had to be 0 and remain 0 throughout the subsequent visits.
Efficacy Results from Proof of Concept Clinical Study
The study was planned to identify and evaluate 220 patients with confirmed adenoviral infection divided between NVC-422 and the control group. However, the study was concluded early based on lower-than-expected rate of enrollment of adenoviral-positive patients and an interim analysis of the primary efficacy variable (microbiological eradication on day 5 and or 7) in 50 adenovirus-positive patients. This analysis led Alcon to conclude that the primary microbiological endpoint would not be reached. The results of the study were released on May 18, 2011.
The study proscribed a difference of 20% between NVC-422 and its vehicle in patients with adenoviral conjunctivitis as measured by the primary endpoint (sustained microbiological success)at day 5 and or day 7; this was the definition of a successful study. There were a total of 81 adenoviral conjunctivitis patients (42onNVC-422 and 39 on vehicle) when the study was terminated. As can be seen in the enclosed table, the difference was only 6.6% and the study did not meet its primary endpoint.
Table Oph1.Sustained Microbiological Success in Adenoviral Conjunctivitis Patients
|
NVC-422 (N=42) |
Vehicle (N=39) |
Difference |
|
|
Day 18 |
81.0% |
74.4% |
6.6% |
Another endpoint was sustained clinical cure, which was defined as the combination of one sign (bulbar injection) and one symptom (foreign body sensation) being reduced to zero and staying at zero through day 18. As shown in the next table, at Day 18 the difference was 7.2%.
Table Oph2.Sustained Clinical Cure in Adenoviral Conjunctivitis Patients
|
NVC-422 (N=42) |
Vehicle (N=39) |
Difference |
|
|
Day 18 |
66.7% |
59.5% |
7.2% |
Additional Subset Analysis
In looking further into the data generated by this study, it was recognized that the effects on the EKC patients (a subset consisting of 30 of the 81 adenoviral patients) showed a larger difference between NVC-422 and vehicle. The sustained microbiological success and the sustained clinical cures are presented in the next two tables.
Table Oph3.Sustained Microbiological Success in EKC Patients
|
NVC-422 |
Vehicle |
Difference |
|
|
Day 18 |
76.5% |
61.5% |
15.0% |
Table Oph4.Sustained Clinical Cure in EKC Patients
|
NVC-422 |
Vehicle |
Difference |
|
|
Day 18 |
68.8% |
53.9% |
14.9% |
The most dramatic differences between NVC-422 and its vehicle in EKC patients was clearing of the patients’ blurred vision. The difference between NVC-422 and Vehicle was greater than 30% for all visits (ranged from 30.8.0% to 49.0% with an average of 41.2%).
Table Oph5.Sustained Resolution of Blurred Vision in EKC Patients
|
NVC-422 (N=13) |
Vehicle (N=8) |
Difference |
|
|
Day 3 |
30.8% |
0.0% |
30.8% |
|
Day 5 |
46.2% |
12.5% |
33.7% |
|
Day 7 |
61.5% |
12.5% |
49.0% |
|
Day 9 |
69.2% |
25.0% |
44.5% |
|
Day 11 |
84.6% |
37.5% |
47.1% |
|
Day 18 |
92.3% |
50.0% |
42.3% |
The most clinically troublesome effect seen in EKC is the appearance of sub-epithelial infiltrates or SEIs that occur towards the end of the active infectious phase. SEIs can impair and blur vision quite severely and may last for weeks or months. This is why EKC is considered to be sight threatening. In the 30 EKC patients, NVC-422 had two very beneficial effects (as compared to its vehicle) on SEIs. In those patients who developed SEIs, there was greater percentage of eyes in which SEIs were resolved by Day 18. In the eyes that still had SEIs at Day 18, the average number of SEIs was less than in the vehicle treated eyes.
Table Oph7.Effect of NVC-422 on SEIs in EKC Patient Eyes
|
NVC-422 |
Vehicle |
|
|
Eyes with SEIs Resolved - Day 18 |
60% |
30% |
|
Average SEI Score - Unresolved on Day 18 |
1.25 |
1.43 |
Finally, this proof-of-concept study generated data supporting the hypothesis that in the cases of unilateral infection (at time of entry into the study) administration of the NVC-422 may reduce the spread of infection to the fellow eye (see table below). This data is derived from the 55 AITT patients with unilateral infections on Day 1.
TableOph7.Effect of NVC-422 on the Spread of Infection to Fellow Eye
|
NVC-422 (N=31) |
Vehicle (N=24) |
Difference |
|||
|
N= |
% |
N= |
% |
% |
|
|
Fellow Eye Was Not Infected through Day 18 |
8 |
19.4 |
2 |
8.3 |
11.1 |
Safety Findings from Proof of Concept Clinical Study
NVC-422 was well-tolerated and safe, with the most frequent treatment-related adverse events being eye irritation in 14.2% of patients versus 1.3% for placebo. Most events were assessed as mild or moderate in intensity and the majority resolved without treatment. Approximately 5% of patients discontinued for both treatment and non-treatment-related adverse events in the 452 treated patients.
NovaBay’s Interpretation of Phase II Data
After careful review of all the safety and efficacy data from the proof-of-concept clinical study, NovaBay believes that NVC-422 demonstrated particularly good efficacy in EKC patients, sufficient to warrant further development and clinical studies.
The EKC form of adenoviral conjunctivitis is the most sight-threatening form of the infection. This can damage to the cornea by through forming sub-epithelial infiltrates. These are superficial corneal inflammatory deposits resulting from an immune-mediated reaction which can persist for weeks to months. These sub-epithelial infiltrates may result in decreased visual acuity, foreign body sensation, glare and light sensitivity.
NovaBay strongly believes that the positive effects of NVC-422 in resolving blurred vision resulting from SEIs are of great importance to the patients. This symptom, which begins early after the appearance of signs and symptoms of the infection, is frequently the trigger that causes a person to seek out an ophthalmologist. Secondly, NVC-422 reduced the number and severity of SEIs (as compared to vehicle). This, too, is a clinically important finding to be confirmed in the next safety and efficacy study.
The Second Safety and EfficacyTrial is Underway
On May 4, 2012 the first patient was enrolled into the NovaBay’s new Phase 2b study for adenoviral conjunctivitis called BAYnovation. BAYnovation is a global study anticipated to enroll approximately 450 patients with confirmed adenoviral conjunctivitis at investigational sites in the United States, India, and Brazil. The estimated completion date is Q2, 2013.
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the clinical and microbiological efficacy and safety of NVC-422 compared to vehicle for adenoviral conjunctivitis. Adults and children one year of age and older with adenoviral conjunctivitis in at least one eye may be eligible. Subjects will be randomly assigned to receive either NVC-422 or vehicle. Six visits will be required for this study.
Eligible patients must be one years of age or older and have shown symptoms of viral conjunctivitis in at least one eye for 3 days or less. Inclusion criteria are:
- Signs and symptoms of viral conjunctivitis in at least one eye for 3 days or less,
- Bulbar conjunctival injection,
- and other inclusion criteria per protocol
The exclusion criteria are:
- Presence of sub epithelial infiltrates (SEIs) at the Day 1 visit in either eye,
- Suspected bacterial, fungal, herpes, Chlamydia or Acanthamoeba co-infection, based on clinical observation,
- and other exclusion criteria per protocol
In BAYnovation, the primary efficacy outcome measure is sustained clinical cure at day 18. Additional secondary measures will be assessed including eradication of adenovirus as determined by PCR. Safety appears not to be an issue as over 225 patients have been exposed to this drug in the ocular studies previously conducted.
Market Size
Patients presenting with pinkeye and the other symptoms of infectious conjunctivitis may have either viral or bacterial conjunctivitis. Most often, they are first seen and treated by pediatricians, primary care physicians, internists and optometrists. The physician generally makes a diagnosis based on visual signs and symptoms. In the case of bacterial conjunctivitis, one cannot know the species of microorganism involved without taking an ocular specimen and sending off to a clinical lab for processing. In the case of adenoviral etiology, the Adeno Detector test can be used since it is FDA approved and CLIA waved. This is an in office test which takes 10 minutes to develop after the specimen is collected.
There is no approved or effective therapy for viral conjunctivitis. In practice most patients, whether they are suffering from viral or bacterial conjunctivitis, are prescribed one of the numerous topical antibiotics available. Of course, these are ineffective for viral conjunctivitis. IMS shows that the market for anti-infectives for ophthalmology is comprised of 15.0 million prescriptions annually and NovaBay believes that about half or 7.5 million prescriptions are for viral conjunctivitis and it further estimates that 40% or 3.0 million prescriptions could be for EKC.
NeutroPhase® Wound Cleanser
Summary:
- NeutroPhase® is a proprietary wound cleansing solution containing hypochlorous acid or HOCl.
- The FDA has approved it through the 510(k) process for dermal wound cleansing.
- NeutroPhase is a solution of pure HOCl in saline.
- NeutroPhase is a ready-to-use solution available in convenient 40 mL bottles
- HOCl is known as safe, fast-acting, and broad-spectrum in solution
- HOCl in a solution inactivates P. aeruginosa, E. coli, S. aureus,C. albicans and A. niger.
Background
NeutroPhase is a solution of HOCl that is a safe, fast-acting, broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent. NovaBay’s formulation is a shelf- stable form of HOCI. supplied as 0.01% HOCl in saline solution packaged in glass bottles of various sizes with PTFE lined screw caps.
Indications
The product is indicated for moistening absorbent wound dressings and cleaning minor cuts, minor burns, superficial abrasions and minor irritations of the skin. It is also intended for moistening and debriding acute and chronic dermal lesions, such as Stage I - IV pressure ulcers, stasis ulcers, leg ulcers, diabetic foot ulcers, post-surgical wounds, first and second degree burns, abrasions and minor irritations of the skin.
Safety
NeutroPhase has been demonstrated to be non-irritating and non-sensitizing in GLP animal models. Twenty-eight-day in-vivo toxicity studies were conducted in rodent and non-rodent, full-thickness wound toxicology studies. These used daily applications of NeutroPhase at 0.01%, 0.03% and 0.1% and showed no evidence of systemic toxicity. Wound site histopathology was consistent with wound healing activity. Additional GLP toxicology studies showed no evidence of skin sensitization or eye irritation at any of these concentrations.
Advantages over Competing Products
The first step in the treatment of a chronic wound is to cleanse the wound bed. This can be achieved in a number of ways, but in all cases some form of a wound cleanser or wash is used. The majority of 510k cleared wound cleansers on the market today have drawbacks to their use. These drawbacks include cytotoxicity (killing cells), ineffective antimicrobial activity or short shelf life. Typically, these products include: providone-iodine solutions, chlorhexidine based solutions, silver nitrate solutions, Betadine solutions, Dakin’s solution (sodium hypochlorite solution) and various surfactant based solutions.
NeutroPhase has several advantages over the competing products. NeutroPhase is a solution of pure HOCl in saline with effective concentration of 0.01%. Pure HOCl is 500 times more powerful than NaOCl which is often found in competing products and Dakin solution. Currently data supporting a shelf life of 12 months is available. Stability studies are ongoing to verify extended shelf life.
Previous Research and Clinical Experience
An investigator-sponsored pilot study in patients with chronic non-healing wounds provided a preliminary indication of safety and efficacy. The company has also conducted a pilot study in patients with venous stasis ulcers under an IND.
Manufacturing
Commercial supply manufacturing has been validated and product will be available by the end of 2012.
Intellectual Property
NovaBay has two issued U.S. patents on the use of NeutroPhase and has other applications pending in the U.S. and foreign countries.
Commercial Opportunity
In the United States alone, the NIH estimates that there are over 5 million patients with chronic dermal ulcers. The company is conducting research on other potential applications for NovaBay technology such as pre- and post-operative disinfection, dermatology, dental, severe burns and sinusitis.
The company recently announced a partnership with Pioneer Pharma in mainland China to address that market. NeutroPhase will be manufactured in the US and exported worldwide under the brand name NeutroPhase.
The current marketing strategy is to export globally to pharmaceutical partners worldwide with sales and marketing organizations. The partnership with Pioneer Pharma brings 1000 sales reps with access to 7500 hospitals and 40,000 pharmacies.
Partnerships on other international territories are being negotiated. NovaBay will be responsible for registering the product in China, and we will be exporting from the US to China as a finished product. The total process for registration typically takes about 18 months in China.
Tagged as NovaBay + Categorized as Company Reports




